Appendix
Installing OpenRTM-aist 1.2 (Windows、using msi Installer)

Install dependent software
You must install Python before installing OpenRTM-aist. You need to install the 32-bit version of Python when installing the 32-bit version of OpenRTM-aist, and install the 64-bit version of Python when installing the 64-bit version of OpenRTM-aist.
Install OpenRTM-aist
Download and install the installer from the link below, OpenRTM-aist-1.2.x-RELEASE_x86_64.msi for the 64-bit version, and OpenRTM-aist-1.2.x-RELEASE_x86.msi for the 32-bit version.
Install JDK8
Communication middleware called CORBA is required to execute OpenRTM-aist-Java. In Java, CORBA functionality was originally included as a standard function, but since Java 9 it is treated as deprecated (the deprecated function that will be removed in the future) and will be completely removed in Java 11 and later. Therefore, to use OpenRTM-aist-Java, it is necessary to use the Java 8 development environment package JDK8. Original developer Oracle is decreasing the support of JDK8 (Oracle had already stopped the update support for free commercial users and will stop it to non-commercial user in 2020). But many people still need Java8, so JDK8 itself is available for some time from several vendors. Here, we will introduce how to obtain and install JDK8.
JDK8 distributors
Here are some of the things we found about distributors of JDK8: Please note that it is only a list of some of the ones we have found, and that there are no intentions, if any, are not listed here. Also, there are various conditions, such as the distribution of each site for paid use and support for the fee, so please check each site before using it.
Oracle
As of November 2019, JDK8 download is available from Oracle for the developer and distributor of Java. It seems that personal use and development use have a free license, but commercial use seems to require a paid license. Please refer to the link below and the message from Oracle for the exact license conditions.
- Oracle Java SE Subscription
- JDK8 Download
- These pages may be deleted if Oracle stops distributing Java8.
OpenJDK
OpenJDK is an open-source Java implementation by Oracle, distributed under GPLv2 with Classpath Exception. Most JDK implementations are based on this OpenJDK. There is a button of JDK DOWNLOAD from Java SE 8xxxx (xxxx is u231 as of November 2019) from the link below, so click it and get the one that is suitable for your platform.Adopt Open JDK
AdoptOpenJDK is a project to provide an OpenJDK build sponsored by IBM and maintained by the community. Two types of JVMs are provided, one developed by the OpenJDK community called HotSpot and the other developed by the Eclipse community called OpenJ9.
Select [OpenJDK8 (LTS)] and JVM ([HotSpot] or [OpenJ9]) from the link below and click the [Latest release] button. The download for the platform should begin. If you want something for a different platform, click the [Other platforms] button to get the required JDK. For information on how to install, please refer to the link [Installation].Amazon Open JDK
Amazon Corretto is a build of OpenJDK that includes Amazon's long-term support. Go to the website from the link below and click the [Download Amazon Corretto8] button. A list of builds for each platform will be displayed. Get the necessary installation files for your platform.
Installation in Linux environment
Get the package from the repository
OpenJDK packages equivalent to JDK8 are distributed as standard packages in major Linux distributions.
Ubuntu / Debian / Raspbian
On Ubuntu Linux, Debian Linux, etc., you can install using the apt command as follows.
$ sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
Fedora
In Fedora Linux, you can install with yum command as follows.
$ sudo yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk
Other than obtaining the package from the repository
It can also be obtained from the Web site of the above third party vendor. Follow the information on the site for the installation method, or install using the standard Java method.
As a reference, here are the steps to download and expand the binary (tar.gz) from Adoptium (formerly AdoptOpenJDK) to the Raspberry Pi OS bullseye 64bit environment and switch from the already installed JDK11 to JDK8.
Download JDK8 for aarch64.
$ wget https://github.com/adoptium/temurin8-binaries/releases/download/jdk8u352-b08/OpenJDK8U-jdk_aarch64_linux_hotspot_8u352b08.tar.gz $ tar xvzf OpenJDK8U-jdk_aarch64_linux_hotspot_8u352b08.tar.gz $ ls OpenJDK8U-jdk_aarch64_linux_hotspot_8u352b08.tar.gz jdk8u352-b08
To switch from JDK11 to JDK8 with the update-alternative command, copy it under /usr/lib/jvm/ and create and register a symbolic link with the --install option.
$ sudo mv ./jdk8u352-b08 /usr/lib/jvm/jdk8u352 $ sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/java" "java" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk8u352/bin/java" 1 $ sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javac" "javac" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk8u352/bin/javac" 1
Now switch to JDK8 with the sudo update-alternative --config java command shown in "When other than JDK8 is already installed" below. Check the version after switching.
$ java -version openjdk version "1.8.0_352" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (Temurin)(build 1.8.0_352-b08) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (Temurin)(build 25.352-b08, mixed mode)
When other than JDK8 is already installed
Note that a JDK other than JDK8 may be installed in the default state.
$ java -version
Make sure that the command version is JDK8, such as the version starting with 1.8. If not
$ sudo update-alternative --config java
Use the command to select a Java environment based on JDK8. The execution example after installing openjdk-8-jdk in the environment of ubuntu18.04 is as follows.
$ sudo update-alternatives --config java Choice Path Priority Status -------------------------------------------------- ---------- * 0 /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1111 automatic mode 1 /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1111 Manual mode 2 /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java 1081 Manual mode Press <Enter> to keep the current selection [*], otherwise press the number of the choice: 2 update-alternatives: use/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java in manual mode to provide /usr/bin/java (java)
Installation on Windows environment
To install JDK8 on Windows, obtain the MSI file from the above site and execute it to install it, or for files other than MSI, install according to the instructions of the source. After installation, open the command prompt as in the case of Linux above
java -version
And confirm the installation.
Bulk installation script
Where to get the bulk installation script
Where to get the installation scripts provided by openrtm.org. Right-click the following link and select [Copy Link URL] (for Firefox) to get the URL and download it with a command such as wget (the method is shown below), or [Name Select "Save link as" (for Firefox) and download. Please execute the downloaded script with root authority. In these scripts, the necessary packages are installed sequentially using apt-get (in Ubuntu, Debian, and Raspbian case).
- Bulk installation script for Ubuntu
- Bulk installation script for Debian
- Bulk installation script for Raspbian
- Bulk installation script for Fedora
This script can be installed by specifying the options, according to the purpose.
However, this script installs all packages related to OpenRTM-aist, so unnecessary packages may also be installed. If you are familiar with it, you can also install it manually.
※Please check the version number of scripts for Ubuntu and Raspbian.
If you install OpenRTM-aist 1.2.2 for Python3, you need to use the corresponding script, so check the version number. You can check the version number as follows. If you cannot get the version number, it is an old script.
You need 2.0.0.05 or higher for Ubuntu and 2.0.0.03 or higher for Raspbian.
$ sh pkg_install_ubuntu.sh --version 2.0.0.05
$ sh pkg_install_raspbian.sh --version 2.0.0.03
pkg_install_{ubuntu|debian|raspbian}.sh
The available options are the same, but pkg_install_raspbian.sh does not support openrtp installation. Therefore, openrtp cannot be used as an argument of the -l option. ※The -t option only supports ubuntu and raspbian.
Option list
Usage:
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l {all|c++} [-r|-d|-s|-c] [-t OpenRTM-aist old version number] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l {python} [-r|-d|-c] [-t OpenRTM-aist old version number] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l {java} [-r|-d|-c] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l {openrtp|rtshell} [-d] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh {--help|-h|--version}
Example:
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh [= pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l all -d]
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l all -d
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l c++ -c --yes
pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l all -u
Options:
-l <argument> language or tool {c++|python|java|openrtp|rtshell|all}
all install packages of all the supported languages and tools
-r install robot component runtime
-d install for robot component developer [default]
-t <argument> OpenRTM-aist old version number
-s install tool packages for building from the source code
-c install tool packages for core developer
-u uninstall packages
--yes force yes
--help, -h print this
--version print the version numberWhere "-l all" specifies that packages for all supported languages and tools will be installed.
By specifying the option, the package shown below will be installed.
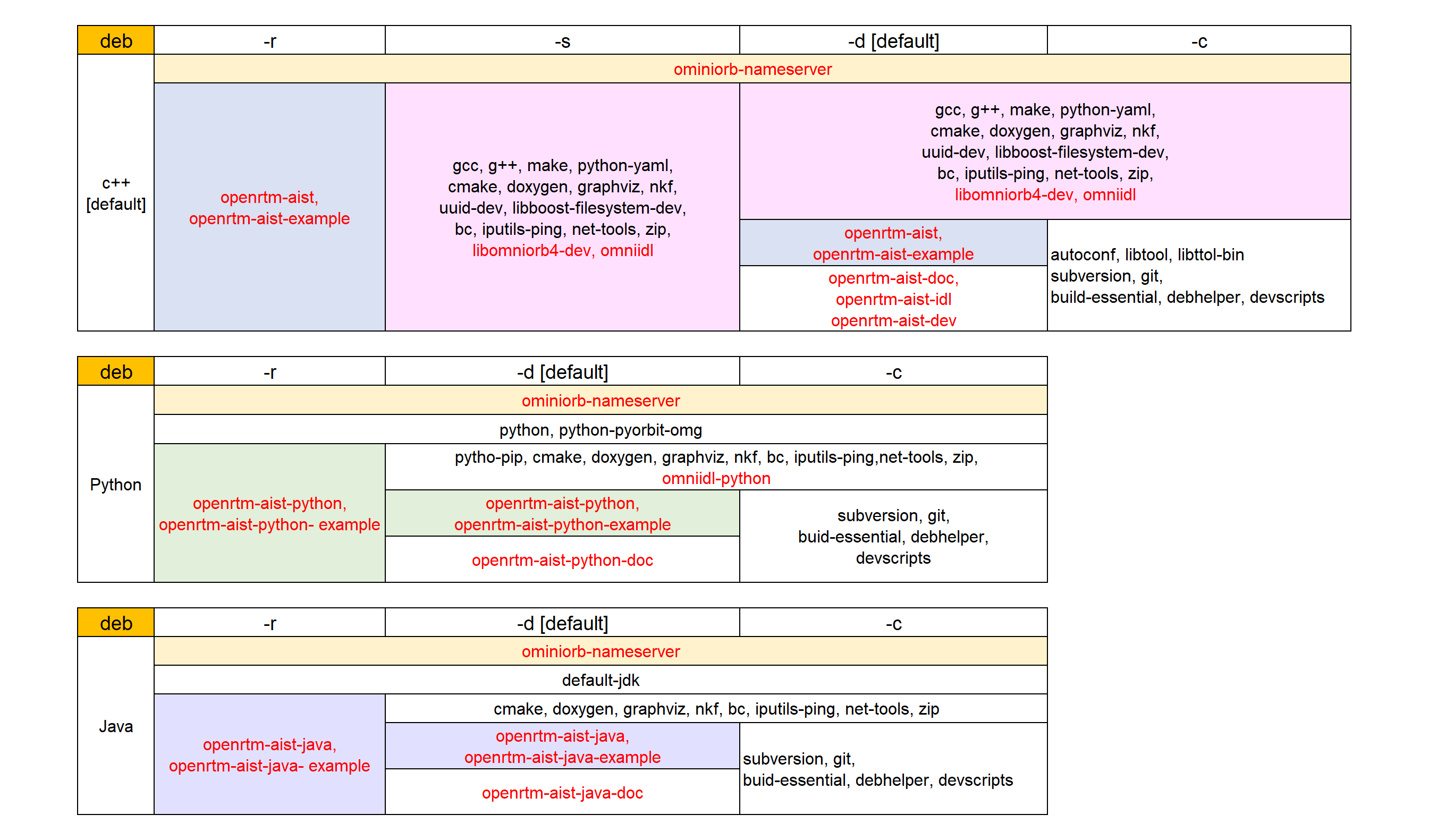
List of deb packages to be installed
Red letters indicate packages that are uninstalled when -u (uninstall) is specified.
※Since OpenRTM-aist 1.2.2 has changed the Python version from 2 series to 3 series, the packages to be installed are as follows.
omniidl-python3 openrtm-aist-python3 openrtm-aist-python3-example openrtm-aist-python3-doc
pkg_install_fedora.sh
Option list
Usage:
pkg_install_fedora.sh -l {all|c++} [-r|-d|-s|-c] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_fedora.sh [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_fedora.sh -l {python|java} [-r|-d|-c] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_fedora.sh -l {openrtp|rtshell} [-d] [-u|--yes]
pkg_install_fedroa.sh {--help|-h|--version}
Example:
pkg_install_fedora.sh [= pkg_install_fedora.sh -l all -d]
pkg_install_fedora.sh -l all -d
pkg_install_fedora.sh -l python -c --yes
Options:
-l <argument> language or tool {c++|python|java|openrtp|rtshell|all}
all: install packages for all the supported languages and tools
-r install robot component runtime
-d install for robot component developer [default]
-s install tool packages for building from the source code
-c install tool packages for core developer
-u uninstall packages
--yes force yes
--help, -h print this
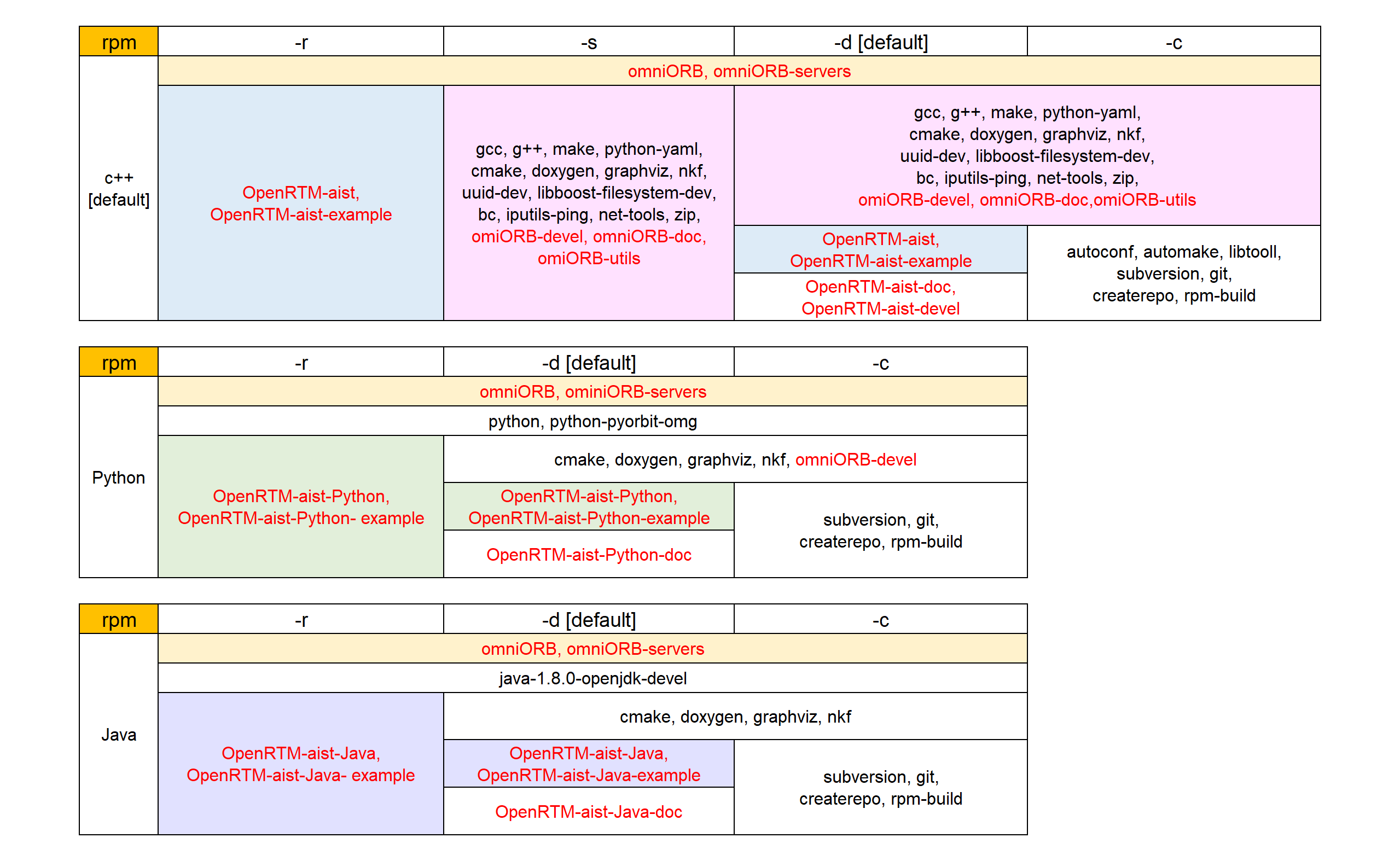
--version print the version numberList of rpm packages to be installed
Red letters indicate packages that are uninstalled when -u is specified.
How to use batch installation script
Below are the download and installation method using the batch installation script. (Replace "ubuntu" with "debian", "raspbian", or "fedora", depending on the distribution you are installing.)
Download the batch installation script for your environment using the following command.
$ wget <Download URL of pkg_install_ubuntu.sh>
Install C ++ version
This is a recommended input example for those who install the C ++ version for the first time. Specify the target language by adding only the option "-l" and perform a default installation without specifying any other options (or with the -d option).
$ sudo sh ./pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l c ++
Install Python version (omit "Y" input)
This is a recommended input example for those who install the Python version for the first time. By adding the option "--yes", you can skip the installation confirmation question and enter "Y". No other options are specified, so the same ones specified with the -d option will be installed.
$ sudo sh ./pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l python --yes
Install packages required for C ++ version, Python version and core development (Development of OpenRTM-aist itself)
Install the packages required for core development by adding the option "-c", and omit the input of "Y" with the option "--yes".
$ sudo sh ./pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l c ++ -l python -c --yes
Uninstall C ++ version
Uninstall the C ++ version by adding the option "-u".
For the packages to be uninstalled, check List of deb packages to be installed and List of rpm packages to be installed.
$ sudo ./pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l c ++ -u
Install the old version (1.2.1)
If the latest version of OpenRTM-aist is 1.2.2, use option "-t" to install the 1.2.1 version. The target is only c++ and python. If you execute it in the environment where 1.2.2 is already installed, it will be downgraded to 1.2.1.
$ sudo ./pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l c++ -t 1.2.1 $ sudo ./pkg_install_ubuntu.sh -l python -t 1.2.1